Hollywood
Horror & Thriller
International News
Judgments & Cases
News
United States of America
Web Series
News
- The world’s first comprehensive laws to regulate artificial intelligence (AI) have been agreed in a deal between the European Parliament and EU member states.
Why do we need rules on AI?
- Ethical Concerns: AI systems can make decisions and take actions that impact individuals and society. Establishing rules helps address ethical concerns related to the use of AI, ensuring that it aligns with human values and respects fundamental rights.
- Privacy: AI often involves the processing of large amounts of data. Rules can help protect individual privacy by specifying how data should be collected, stored, and used.
- Security: Rules are necessary to ensure the security of AI systems. This includes safeguarding against potential vulnerabilities and protecting against malicious uses of AI technology.
- Transparency: Rules can mandate transparency in AI systems, requiring developers to disclose how their algorithms work.
- Competition and Innovation: Establishing a regulatory framework provide a level playing field for businesses, preventing the abuse of market dominance and encouraging responsible innovation.
- Public Safety: In cases where AI is used in critical domains such as healthcare, transportation, or public infrastructure, rules are essential to ensure the safety of individuals and the general public.
The EU framework
- The legislation includes safeguards on the use of AI within the EU, including guardrails on its adoption by law enforcement agencies.
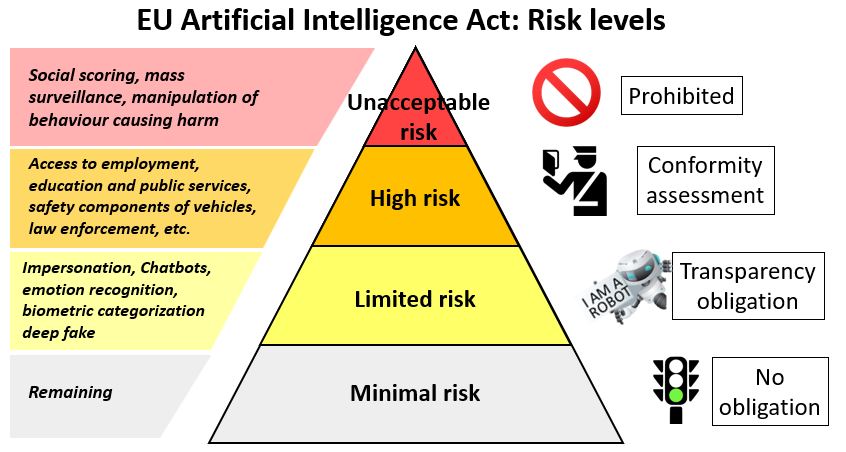
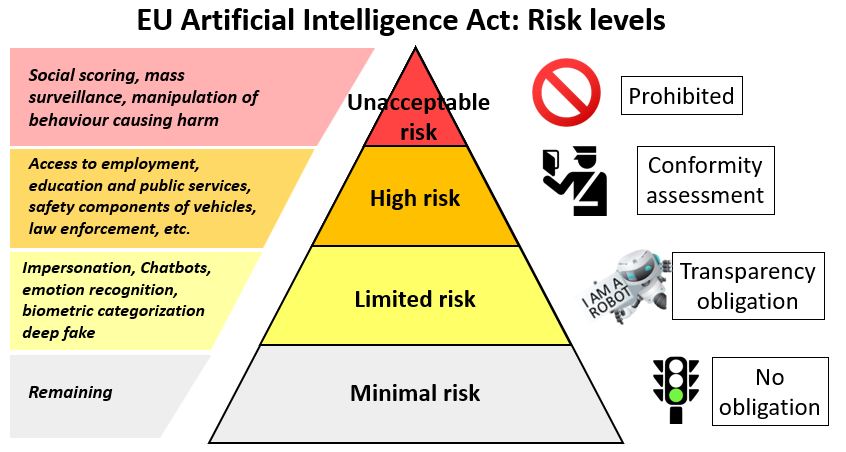
- Levels of risk: The Regulatory Framework establishes obligations for providers and users depending on the 4 levels of risk from artificial intelligence i.e. Unacceptable risk, High risk, Limited risk, Minimal or no risk.
Unacceptable risk
- Unacceptable risk AI systems are systems considered a threat to people and will be banned. They include:
- Cognitive behavioral manipulation of people or specific vulnerable groups: for example voice-activated toys that encourage dangerous behavior in children
- Social scoring: Classifying people based on behavior, socio-economic status or personal characteristics
- Real-time and remote biometric identification systems, such as facial recognition.
- Exception: Governments can only use real-time biometric surveillance in public areas when there are serious threats involved, such as terrorist attacks.
High risk
- AI systems that negatively affect safety or fundamental rights will be considered high risk and will be divided into two categories:
- AI systems that are used in products falling under the EU’s product safety legislation. This includes toys, aviation, cars, medical devices and lifts.
- AI systems that will have to be registered in an EU database and fall into eight specific areas including Biometric identification and categorisation of natural persons, Management and operation of critical infrastructure, Education and vocational training, law enforcement etc.
- All high-risk AI systems will be assessed before being put on the market and also throughout their lifecycle.
Limited risk
- Limited risk AI systems should comply with minimal transparency requirements:
- Disclosing that the content was generated by AI,
- Designing the model to prevent it from generating illegal content,
- Publishing summaries of copyrighted data used for training.
- User Discretion: After interacting with the applications, the user can then decide whether they want to continue using it.
- User awareness: Users should be made aware when they are interacting with AI. This includes AI systems that generate or manipulate image, audio or video content, for example deepfakes.
Minimal or no risk
- The proposal allows the free use of minimal-risk AI.
- This includes applications such as AI-enabled video games or spam filters.
| What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? – Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. – AI works by analyzing large amounts of labeled training data to find patterns and correlations. – It requires specialized hardware and software, with popular programming languages like Python, R, Java, C++, and Julia often used by developers. – AI programming focuses on cognitive skills like learning, reasoning, self-correction, and creativity to achieve specific tasks, such as generating new text, images, music, and ideas. |
