World-Location-Based Topics for UPSC Civil Services Exam by Global Updates Now
Contents
Congo River (formerly Zaire River) 7
Lakes in the Albertine Rift 12
Other Major Lakes in Africa 13
Major Mountain Ranges of Africa 13
Other major deserts of Africa 15
Recently in News (Focus Area for Prelims 2020) 16
Important Points are highlighted in Blue and Red
Trying to mug up all the facts is counterproductive. Focus only on those that are recently in news.
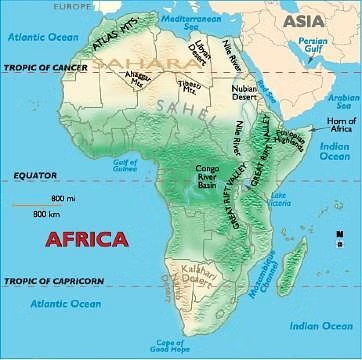
Africa
| Area | • 30.3 million km2 (6% of Earth’s total surface area and 20% of its land area) |
| • Algeria is Africa’s largest country by area. | |
| • The majority of the continent and its countries are in the Northern Hemisphere. | |
| Countries | • Total 54 |
| • Largest countries: Algeria, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sudan, Libya & | |
| Chad. | |
| • Smallest countries: Seychelles, São Tomé and Príncipe, Mauritius, Comoros & | |
| Cape Verde. | |
| • Smallest countries in mainland Africa: Gambia, Eswatini (Swaziland), Djibouti, | ||||
| Rwanda & Burundi. | ||||
| Population | • | 1.3 billion | ||
| • Nigeria is Africa’s largest country by population. | ||||
| • Largest countries by population: Nigeria, Ethiopia, Egypt, Democratic Republic | ||||
| of the Congo & Tanzania. | ||||
| • Africa’s average population (19.7 years) is the youngest amongst the continents. | ||||
| Longitudinal Extent | 51° E to 17° W (~7,400 km — Ras Hafun in Somalia to Cape-Vert in Senegal) | |||
| of the Mainland | ||||
| Latitudinal Extent of | 37° N to 34° S (~8,000 km — Ras ben Sakka in Tunisia to Cape Agulhas in South Africa) | |||
| the Mainland | ||||
| Coastline | • The coastline of Africa is 30,500 km in length. | |||
| • The coastline of Africa is shorter than that of Europe (38,000 km), because | ||||
| there are few inlets and few large bays or gulfs. | ||||
| Major Cities | • Lagos (Nigeria), Kinshasa (Congo), Cairo, Giza & Alexandria (Egypt), Johannes- | |||
| burg, Pretoria & Durban (South Africa), Nairobi (Kenya), Casablanca & Rabat (Mo- | ||||
| rocco), Algiers (Algeria), Addis Ababa (Ethiopia), Kano (Nigeria), Bamako | ||||
| (Mali), Mogadishu (Somalia), Mombasa (Kenya), Harare (Zimbabwe), Tripoli | ||||
| (Libya), Kigali (Rwanda), Tunis (Tunisia) & Benghazi (Libya). | ||||
| • Largest by Area: Lagos & Cairo. | ||||
| • | Largest by Population: Lagos, Kinshasa & Cairo . | |||
| • Pietermaritzburg: On 7 June 1893, young Mahatma Gandhi was thrown out of a | ||||
| train at Pietermaritzburg station. | ||||
| • Addis Ababa: Headquarters of the African Union. | ||||
| Major Islands/Island | • Madagascar, Comoros, Seychelles, Mauritius, Reunion (overseas territory of | |||
| groups | France), Cape Verde Islands, Canary Islands (Spain), São Tomé & Príncipe & | |||
| Madeira Islands (Portugal). | ||||
| Major Lakes | • Largest lakes by surface area in Africa: 1) Lake Victoria 2) Lake Tanganyika 3) | |||
| Lake Malawi (all freshwater lakes) | ||||
| • Largest lake by volume in Africa: 1) Lake Tanganyika 2) Lake Malawi 3) Lake | ||||
| Victoria | ||||
| • Deepest lake in Africa: 1) Lake Tanganyika (2nd deepest lake in the world. | ||
| Lake Baikal in Russia is the deepest lake) 2) Lake Malawi | ||
| Highest Mountains | 1. | Mount Kilimanjaro (5895 m) |
| 2. | Mount Kenya (5199 m) | |
| Longest Rivers | 1. | Nile River (Baḥr Al-Nīl – 6,853 km – headwaters of Kagera River to Nile Delta) |
| 2. | Congo River (4,700 km) | |
| 3. | Niger River (4,200 km) | |
| 4. | Zambezi River | |
Major Rivers of Africa
Nile River
- The Nile River flows from south to north (Russian rivers Lena River – 4,294 km, Ob River – 3,700 km & Yenisey River – 3,487 km are other major south to north flowing rivers of the world).
- It begins in the rivers that flow into Lake Victoria, and empties into the Mediterranean Sea.
- From Lake Victoria to the Mediterranean, it is more than 6,600 km long, making it the world’s longest river.
- Compared to other major rivers, though, the Nile carries little water.
- Its drainage basin covers eleven countries: Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan, and Egypt.
- Major tributaries: The White Nile, the Blue Nile, and the Atbarah.
White Nile
- The White Nile is considered to be the headwaters and primary stream of the Nile itself.
- The source of the White Nile is sometimes considered to be Lake Victoria.
- But Kagera River, which flows into Lake Victoria is a significant feeder river.
- Hence, the length of Nile is sometimes considered from the headwaters of the Kagera River.
- Kagera River, the largest tributary of L. Victoria, rises in Burundi near the northern tip of Lake Tanganyika.
- At Khartoum (capital of Sudan) the White Nile is joined by the Blue Nile.
- Mountain Nile: Lake No in South Sudan, the confluence of the Mountain Nile (Bahr al Jabal) and Bahr el Ghazal rivers, marks the transition between the Mountain Nile and White Nile proper.
Aswan High Dam
- The Aswan High Dam is an embankment dam built across the Nile in Egypt, between 1960 and 1970.
- Lake Nasser is the man-made lake formed by the construction of the Aswan Dam.
- Asan Dam is developed to better control flooding, provide increased water for irrigation and hydroelectricity.
- The High Dam has had a significant effect on the economy of Egypt.
- However, the silt and sediment, crucial for the replenishment of the lower reaches and the delta, is now building up behind the Aswan dam instead.
- Instead of growing in size through the soil deposits, the delta is now shrinking due to erosion.
- In addition, routine annual flooding no longer occurs along parts of the Nile.
- These floods were necessary to flush and clean the water and to replenish the soils.
Blue Nile
- The Blue Nile is the most significant tributary of the Nile.
- Though shorter than the White Nile, ~60% of the water that reaches Egypt originates from the Blue Nile.
- The White Nile supplies just 15 percent of the total volume entering Lake Nasser.
- Blue Nile originates in Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands.
- The river flows through Sudan to join the White Nile at Khartoum.
Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam
- Egypt has been in virtual control of the Nile water for centuries.
- Almost 86% of the water reaching Egypt originates from Ethiopia.
- Egypt takes 66% of the Nile’s water and Sudan 22%, and the remaining is lost to evaporation.
- Despite Ethiopia’s massive contribution, its use of the water from the river system is almost nothing.
- Egypt is now alarmed by Ethiopia’s Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (largest hydroelectric dam in Africa).
- After a major water-war scare, Egypt, Ethiopia, and Sudan agreed on a deal for managing the dam.
Atbarah River
- The Atbarah River (Black Nile) flows into Nile at Atbarah, 200 miles north of Khartoum.
- It rises in northwest Ethiopia, approximately 50 km north of Lake Tana.
- The Atbarah is the last tributary of the Nile before it reaches the Mediterranean.
Congo River (formerly Zaire River)
- Congo River (4,700 km) is Africa’s second longest river, after the Nile.
- It rises in the highlands Zambia between Lakes Tanganyika and Lake Malawi as the Chambeshi River.
- Its drainage basin (4,000,000 km2) covers Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), as well as most of the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, Cameroon, Zambia, Angola and Tanzania.
- Kinshasa (capital of DRC), is situated on the left bank of the Congo River.
- Brazzaville (capital of Republic of the Congo), is situated on the right bank.
Niger River
- Niger River (4,200 km) is the third longest river in Africa, after the Nile and the Congo.
- Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea.
- It runs in a crescent through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through Niger Delta into Gulf of Guinea.
Zambezi River
- The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa and the longest east-flowing river in Africa.
- The river crosses/forms the boundaries of Angola, Zambia, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe & Mozambique.
- Kariba and Cahora Bassa dams, two of Africa’s largest hydroelectric projects, are on the Zambezi River.
Victoria Falls
- The Zambezi’s most noted feature is Victoria Falls.
- Victoria Falls is located on the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe.
- It is considered to be one of the world’s largest waterfalls due to its width of 1,708 metres.
- It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Orange River
- The Orange River is a river in Southern Africa.
- It is the longest river within the borders of South Africa.
- Orange River Basin extends extensively from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north.
- It rises in the Drakensberg mountains in Lesotho.
- The river forms part of the international borders between South Africa and Lesotho and between South Africa and Namibia.
Great Rift Valley
- The Great Rift Valley runs for ~6,400 km from northern Syria (Asia) to central Mozambique (East Africa).
- The northernmost part of the Rift forms the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon.
- Farther south, the valley is the home of the Jordan River which continues south through the Jordan Valley into the Dead Sea on the Israeli-Jordanian border.
- From the Dead Sea southward, the Rift is occupied by the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea.
- The Afar Triangle of Ethiopia and Eritrea is the location of a triple junction.
- The Gulf of Aden is an eastward continuation of the rift, and from this point, the rift extends south-eastward as part of the mid-oceanic ridge of the Indian Ocean.
East African Rift Valley
- In a southwest direction from the triple junction, the fault continues as East African Rift Valley, which split the older Ethiopian highlands into two halves.
- The East African Rift Valley transects through Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Zambia, Tan-zania, Malawi and Mozambique.
- Before rifting, enormous continental flood basalts erupted on the surface and uplift of the Ethiopian, Soma-lian, and East African plateaus occurred.
- East African Rift Valley divides into the Eastern Rift and the Western Rift.
- The Eastern Rift (also known as Gregory Rift) includes the main Ethiopian Rift, which continues south as the Kenyan Rift Valley.
- The Western Rift Valley includes the Albertine Rift, and farther south, the valley of Lake Malawi.
- The Western Rift (Albertine Rift) contains some of the deepest lakes in the world.
Breaking up of Africa
- The East African Rift (EAR) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa.
- To the south, where the rift is young, extension rates are low. Volcanism and seismicity are limited.
- Towards the Afar region, however, the entire rift valley floor is covered with volcanic rocks.
- This suggests that, in this area, the lithosphere has thinned almost to the point of complete break-up.
- The African Plate is in the process of splitting into two tectonic plates, called the Somali Plate and the Nubian Plate (African Plate), at a rate of 6–7 mm annually.
Volcanism and seismicity along East African Rift Valley
- The East African Rift Zone includes many active as well as dormant volcanoes.
- Mount Kilimanjaro, is a dormant stratovolcano in Tanzania, Mount Kenya is an extinct stratovolcano.
- Although most of these mountains lie outside of the rift valley, the EAR created them.
- The EAR is the largest seismically active rift system on Earth today.
- The majority of earthquakes occur near the Afar Depression, with the largest occurring along the faults.
African Great Lakes
- African Great Lakes region (sometimes also called Greater Lakes region) include Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Malawi, Rwanda, Tanzania and Uganda.
Lakes that drain into the White Nile river
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Albert
- Lake Edward
Lakes that drain into the Congo River
- Lake Tanganyika
- Lake Kivu
Lakes that drain into the Zambezi via the Shire River
- Lake Malawi
Endorheic lakes
- Lake Turkana
- Lake Chad
African Great Lakes (MellonDor, from Wikimedia Commons)
Lakes in the Albertine Rift
Lake Victoria
- Lake Victoria is the world’s second largest freshwater lake by surface area (Lake Superior in the largest).
- It is also the world’s largest tropical lake.
- The lake’s area is divided among Tanzania, Uganda & Kenya.
- The only outflow from Lake Victoria is the White Nile River.
- The uppermost section of the White Nile is generally known as the Victoria Nile until it reaches Lake Albert.
Lake Tanganyika
- Lake Tanganyika, the second largest freshwater lake by volume (Lake Baikal in Russia is the largest), is in the Albertine Rift.
- It is also the world’s longest freshwater lake and the second deepest lake in the world (Lake Baikal in Russia is the deepest).
- The lake is shared between Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Burundi, and Zambia.
Lake Malawi (Lake Nyasa)
- Lake Malawi is the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system.
- It is located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
- It is the second deepest lake in Africa, after Lake Tanganyika.
Other Lakes in the Albertine Rift
- Lake Albert & Lake Edward are located on the border between Uganda and the DRC.
- Lake Albert is the northernmost of the chain of lakes in the Albertine Rift.
- Lake Edward is the smallest of the African Great Lakes.
- Lake Kivu lies on the border between the DRC and Rwanda.
Other Major Lakes in Africa
Lake Turkana in Kenyan Rift
- Lake Turkana is a lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, in northern Kenya.
- It is the world’s largest permanent desert lake and one of the largest alkaline lakes.
- It is an endorheic lake (no outflow to other external bodies of water).
Lake Chad
- Lake Chad is located at the conjunction of Chad, Cameroon, Nigeria, and Niger.
- It is a shallow endorheic freshwater lake.
- Lake Chad is one of the most severely endangered lakes in the world. (Central Asia’s Aral Sea & Israel’s
Lake Tiberias — also known as the Sea of Galilee — are other notable endangered lakes).
Major Mountain Ranges of Africa
Range
Countries
Highest Point
| Atlas Mountains | Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia | Mount Toubkal (4,167m) |
| Drakensberg | South Africa | Thabana Ntlenyana (3,482m) |
| Ethiopian Highlands | Ethiopia | Mount Abuna Yosef (4,550m) |
Major Deserts of Africa
Sahara Desert
- The desert comprises much of North Africa, excluding the fertile region on the Mediterranean Sea coast, the Atlas Mountains of the Maghreb (Northwest Africa), and the Nile Valley in Egypt and Sudan.
- To the south, it is bounded by the Sahel, a belt of semi-arid tropical savanna.
- The Ahaggar Mountains and the Tibesti Mountains are the major mountains in the desert.
Sahel
- The Sahel is mostly covered in grassland and savanna, with areas of woodland and shrubland.
- The Sahel part of Africa includes northern Senegal, southern Mauritania, central Mali, northern Burkina Faso, south of Algeria, Niger, north of Nigeria, Cameroon and Central African Republic, central Chad, central and southern Sudan, the extreme north of South Sudan, Eritrea, and the extreme north of Ethiopia.
Tafilalt, Morocco
- Considered one of the biggest oases in the world, Tafilalt is located in the Sahara Desert region of Morocco.
- (The largest self-contained oasis in the world is the Al-Ahsa located in south-eastern Saudi Arabia).
Other major deserts of Africa
Kalahari Desert
- The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savannah in Southern Africa covering much of Botswana, parts of Namibia and regions of South Africa.
- The salt pans of the Makgadikgadi Pan (Botswana) and Etosha Pan (Namibia) are located in the Kalahari.
- The only permanent river, the Okavango, flows into the Okavango delta marshes that are rich in wildlife.
Namib Desert
- The Namib stretches for more than 2,000 km along the Atlantic coasts of Angola, Namibia, & South Africa.
Sinai Peninsula
- The Sinai Peninsula is a arid peninsula in Egypt.
- It is situated between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south.
- The Suez Canal separates the peninsula form the mainland Egypt.
- Israel occupied Sinai Peninsula in the aftermath of the 1967 Six-Day War.
- The region was returned to Egypt in 1982 after the implementation of the 1979 Egypt–Israel Peace Treaty.
Suez Canal
- It is a sea-level waterway in Egypt.
- It opened in 1869 (Mahatma Gandhi was born in 1869).
- The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez.
- The United Kingdom and France owned the canal until July 1956.
- Nationalization of Suez Canal by Egypt led to the Suez Crisis of 1956.
- The canal is owned and maintained by the Suez Canal Authority (SCA) of Egypt.
Recently in News (Focus Area for Prelims 2020)
Botswana’s Okavango Delta
- Context: Hundreds of elephants have died mysteriously in Botswana’s Okavango Delta.
- Botswana is currently home to more elephants than any other African country, & southern Africa re-mains a stronghold for 293,000, or 70%, of the estimated remaining African elephants.
- The Okavango Delta is a vast inland river delta in northern Botswana.
- It was inscribed on the World Heritage List in 2014.
Botswana
- Botswana is a landlocked country in Southern Africa.
- Gaborone is the capital and largest city of Botswana.
- Botswana is bordered by South Africa to the south & southeast, Namibia to the west & north, Zimba-bwe to the northeast & Zambia to the north.
- Botswana is the leading diamond-producing country in terms of value, and the second largest in terms of volume (Russia is the largest diamond producer).
- The two important diamond mines are Orapa Mine and Debswana Jwaneng Mine.
Mauritius
- Context: Mauritius Prime Minister Pravind Jugnauth will inaugurate the country’s new Supreme Court build-ing in the island–nation’s capital, Port Louis jointly with PM of India.
- Mauritius is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about 2,000 kilometres off the south-east coast of the Africa.
- Mauritius is the only country in Africa where Hinduism is the largest religion.
- Hindus in Mauritius are the descendants of the Indian indentured labourers brought by the British in the 1840s to work in the sugarcane fields.
- Mauritius remained a primarily plantation-based colony of the United Kingdom until independence in 1968.
- Nowadays, tourism plays a major role in the country’s economy.
Islands in the region
- Mauritius includes the main island of Mauritius and Rodrigues, Agaléga and St. Brandon.
- The capital and largest city, Port Louis, is located on Mauritius.
Mascarene Islands
- The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues form part of the Mascarene Islands, along with nearby Réunion, a French overseas department.
Disputed Islands
- As a British colony, Mauritius included Rodrigues, Agalega, St. Brandon, Tromelin, the Chagos Archipelago, and, until 1906, the Seychelles.
- Sovereignty over Tromelin is disputed between Mauritius and France.
- In 1965, the U.K. split the Chagos Archipelago from Mauritian territory, and some islands from the Seychelles, to form the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).
- The sovereignty of the Chagos is disputed between Mauritius and the UK.
- Diego Garcia (US Naval base), one of the islands in the region, was leased to the United States
- In February 2019, the International Court of Justice issued an advisory opinion ordering the UK to return the Chagos Islands to Mauritius as rapidly as possible, in order to complete the decolonisation of Mauritius.
Dallol geothermal field
- Researchers have found an aquatic environment with complete absence of any form of life.
- The lifeless environment consists of hot, saline, hyperacid ponds of the Dallol geothermal field in Ethiopia.
- The discovery may lead to an improved understanding of the limits of habitability.
Dallol geothermal field in Ethiopia: A.Savin (Wikimedia); Map Source: Google Maps
Nobel Peace Prize for 2019
- Nobel Peace Prize for 2019 was awarded to Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed Ali for his initiative to resolve the border conflict with neighbouring Eritrea.
- Abiy Ahmed worked out the principles of a peace agreement with Isaias Afwerki, the President of Eritrea.
- The peace declarations were signed in Asmara (capital of Eritrea) and Jeddah (Saudi Arabia).
- Abiy Ahmed contributed actively to the normalisation of diplomatic relations between Eritrea and Djibouti.
Ethiopia
- The major portion of Ethiopia lies in the Horn of Africa.
- Ethiopia shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west and Sudan to the northwest.
- Ethiopia is the most populous landlocked country in the world and the second-most populous nation on the African continent (after Nigeria).
Landlocked countries of the world (Source)
- Its capital city, Addis Ababa, serves as the headquarters of the African Union.
Eritrea
- Eritrea is a country in Eastern Africa, with its capital at Asmara.
- It is bordered by Ethiopia in the south, Sudan in the west, and Djibouti in the southeast.
G5 Sahel
- Militant violence has spread across the vast Sahel region, especially in Burkina Faso and Niger, having started when armed Islamists revolted in northern Mali in 2012.
- G5 Sahel is an institutional framework for coordination in security matters in west Africa.
- It was formed on in 2014.
- Member states: Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, and Niger.
Horn of Africa
- The area is the easternmost projection of the African continent.
- It lies along the southern side of the Red Sea and extends hundreds of kilometres into the Gulf of Aden, Somali Sea and Guardafui Channel.
- The locust swarms originate in the desert of Horn of Africa.
Cote d’Ivoire
- JuIy 2019: India-assisted Mahatma Gandhi IT-biotech park free trade zone was inaugurated in Cote d’Ivoire.
- Ivory Coast is a country located on the south coast of West Africa.
- Ivory Coast is also known as Côte d’Ivoire.
- Ivory Coast’s political capital is Yamoussoukro, while its economic capital is the port city of Abidjan.
- It borders Guinea to the northwest, Liberia to the west, Mali to the northwest, Burkina Faso to the northeast, Ghana to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south.
- The official language of the republic is French.
- Coffee and cocoa are the chief source of export.
Global Updates Now
Whatsapp Channel https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaEiNzY8V0trLE6Obj3L
Website: https://globalupdatesnow.in/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/globalupdates96
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/globalupdatesnow/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/globalupdatesnow/
You Tube: https://www.youtube.com/@globalupdatesnow
Some Important Things Help For Your Business !
- Arkuda Digital – http://arkmc.pxf.io/1rkv7B
- Martinic Audio – http://martinic.evyy.net/AWQvjD
- SentryPC – http://sentrypc.7eer.net/VmKMNk
- Vidine-Video Clip Manager – https://vidine.evyy.net/c/5085341/253410/4152?adid=253410&partnerpropertyid=5470231
- MEL Science: http://imp.i328067.net/QyX7az
- Laganoo: http://laganoo.pxf.io/VmK7Jk
- Muc-Off: http://mucoff.sjv.io/g17Ym0
- FitVille: http://thefitville.pxf.io/Wqz7Zn
- Ora Organic : http://oraorganic.pxf.io/oqvQjg
- Renpho :http://renpho.sjv.io/EKPQ5X
- FitVille-UK :http://thefitvilleuk.pxf.io/OrZG6A
- TikTok For Business (Global):http://getstartedtiktok.pxf.io/9g3aqW
- Laganoo :http://laganoo.pxf.io/q4qXoy
- Trifecta Meal Delivery :http://trifectanutrition.llbyf9.net/rQxoWR
- DropshippingXL :http://dropshippingxl.sjv.io/jrgAa5
- Lenovo India :http://lenovo-in.zlvv.net/EKjvA4
- Muc-Off : http://mucoff.sjv.io/LXG3YZ
- Endoca : https://imp.i110150.net/g1xAX5